Eosin Methylene Blue: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Uses and Importance
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) is a critical tool in microbiology that plays a pivotal role in bacterial identification and differentiation. This article dives deep into its components, applications, and significance in scientific research and diagnostics.
What is Eosin Methylene Blue?
Definition and Overview
Eosin methylene blue is a type of selective and differential agar used in microbiology laboratories to isolate and differentiate Gram-negative bacteria, particularly coliforms like Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species.
Composition of the EMB Agar
EMB agar is a mixture of eosin Y, methylene blue, peptones, and sugars such as lactose and sucrose. These components work together to facilitate the selective growth of Gram-negative bacteria while inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria.
Historical Background
First developed in the early 20th century, EMB agar quickly became a standard in clinical and environmental microbiology for its efficiency in identifying pathogenic organisms.
Role of Eosin Methylene Blue in Microbiology
Purpose in Laboratory Testing
EMB agar serves as a medium for isolating and differentiating enteric bacteria based on their ability to ferment lactose or sucrose.
Mechanism of Action
The eosin Y and methylene blue dyes combine to inhibit Gram-positive bacteria while reacting with acid byproducts from lactose fermentation, creating distinct colony colors.
Applications in Bacterial Differentiation
EMB agar is indispensable for detecting fecal contamination in water, identifying pathogens in clinical samples, and studying bacterial physiology in research.
The Components of EMB Agar
Eosin Y
A dye that acts as a pH indicator, turning colonies different colors based on their fermentation activity.
Methylene Blue
This dye further aids in differentiating bacteria and inhibits Gram-positive organisms.
Peptone and Agar Base
The nutrient-rich agar base supports bacterial growth.
Lactose and Sucrose
These sugars are fermentation substrates that produce the distinctive color changes.
How Eosin Methylene Blue Agar Works
Selective Properties
EMB agar selectively inhibits the growth of Gram-positive bacteria, allowing Gram-negative organisms to thrive.
Differential Properties
By distinguishing between lactose fermenters and non-fermenters, EMB agar helps identify bacterial species.
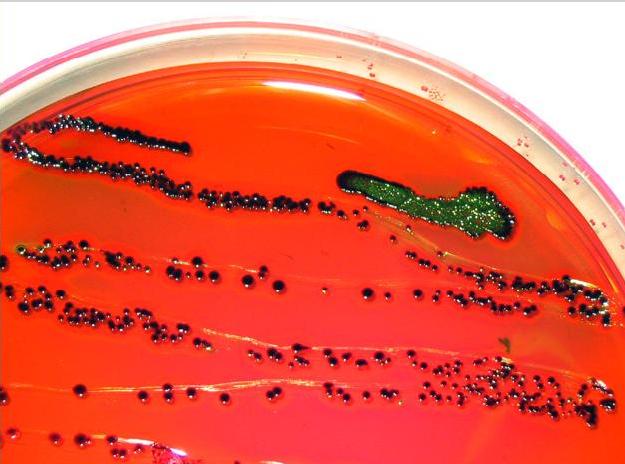
Observing Bacterial Growth Patterns
- Metallic green sheen: Indicates strong lactose fermentation (E. coli).
- Pink/purple colonies: Moderate lactose fermenters (Klebsiella).
- Colorless colonies: Non-fermenters like Proteus or Salmonella.
Common Uses of EMB Agar
Isolation of Gram-Negative Bacteria
EMB agar is widely used to isolate Gram-negative bacteria from mixed cultures.
Identifying Coliforms
It is instrumental in detecting fecal coliforms in environmental samples.
Water and Food Testing Applications
EMB agar is critical in food safety and water quality testing to ensure public health.
Advantages of Using EMB Agar
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: Accurately differentiates bacterial species.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Economical for routine testing.
- Rapid Results: Provides clear results within 24-48 hours.
Limitations of Eosin Methylene Blue Agar
- Gram-Negative Limitation: Cannot detect Gram-positive bacteria.
- Challenges in Interpretation: Ambiguous results may occur with some strains.
- Storage and Preparation Issues: Requires precise conditions for reliability.
Comparison with Other Selective Media
- MacConkey Agar: Similar to EMB but uses neutral red as a pH indicator.
- Hektoen Enteric Agar: Designed for isolating Salmonella and Shigella.
- XLD Agar: Focuses on enteric pathogens with additional indicators.
Safety and Handling Guidelines
To ensure accurate results and maintain safety:
- Store EMB agar in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid contamination during preparation.
- Dispose of used plates properly to prevent biohazards.
Emerging Trends in EMB Agar Research
Research is exploring enhanced EMB formulas to improve bacterial detection and adapting its use for advanced molecular diagnostics.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Eosin Methylene Blue
Eosin methylene blue remains a cornerstone of microbiology, offering unparalleled efficiency in isolating and differentiating Gram-negative bacteria. Its adaptability and reliability make it a staple for professionals in clinical, environmental, and research settings.
FAQs About Eosin Methylene Blue
What is EMB agar primarily used for?
It isolates and differentiates Gram-negative bacteria, especially coliforms.How does it differentiate bacteria?
By their ability to ferment lactose or sucrose, resulting in distinct colony colors.Is EMB agar selective or differential?
It is both selective (for Gram-negative bacteria) and differential (based on fermentation).Can it identify Gram-positive bacteria?
No, EMB agar primarily inhibits Gram-positive organisms.What bacteria produce a metallic green sheen?
Escherichia coli typically produces this distinctive sheen.Are there alternatives to EMB agar?
Yes, alternatives include MacConkey Agar and Hektoen Enteric Agar.
External Resources
Products
-
 Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 50 g
Rated 0 out of 5
Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 50 g
Rated 0 out of 5$120.00Original price was: $120.00.$100.00Current price is: $100.00. -
 Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 20 g
Rated 0 out of 5
Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 20 g
Rated 0 out of 5$70.00Original price was: $70.00.$50.00Current price is: $50.00. -
 Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 10 g
Rated 0 out of 5
Blue Lotus Extract 100:1 – 10 g
Rated 0 out of 5$40.00Original price was: $40.00.$30.00Current price is: $30.00. -
 Organic Dried Whole Blue Lotus Flowers – 100 g
Rated 0 out of 5
Organic Dried Whole Blue Lotus Flowers – 100 g
Rated 0 out of 5$100.00Original price was: $100.00.$80.00Current price is: $80.00. -
 Organic Dried Whole Blue Lotus Flowers – 25 g
Rated 0 out of 5
Organic Dried Whole Blue Lotus Flowers – 25 g
Rated 0 out of 5$30.00Original price was: $30.00.$20.00Current price is: $20.00.
